If you are suffering from asthma, then our treatment for asthma with Homeopathy medicines can help you get cured of asthma. We have helped over 10,200 patients from 108 countries recover from asthma.
See our specialists at any Welling Clinic in India or order online instantly from the link above.
The treatment can reduce and further gradually stop the daily requirement of steroid pumps. Welling Clinic offers specially formulated homeopathy treatment for Asthma to cure permanently. The treatment for asthma has been developed after an exhaustive in-house research and studies. Meet our specialists to know if you too can be cured of asthma with our tailor-made Homeopathy treatment of Asthma.
Get Long-Standing Asthma Cured With Our CUREplus Homeopathy Treatment
Yes, our Homeopathic medicines are best treatment for Asthma cure. It already has, in number of patients. But our specialists need to do your detailed evaluation to see if the treatment can help you too.
- Custom-made Homeopathy medicines for Asthma are proven to cure Asthma in our patients from 108 countries,
- The homeopathy treatment for Asthma can help you stop all major symptoms of Asthma, like sudden attacks of breathlessness, fear of suffocation and prevent hospital visits,
- Once the treatment of Asthma is complete, the symptoms rarely return,
- You get faster relief due to our newly researched homeopathy medicines at Welling Research Labs.
Call +91 9999064336 to book an appointment or to consult and order online. Consult our specialists today for a detailed evaluation and to start your customised Homeopathy medicines for Asthma.
What is Asthma?
Asthma is a chronic lung disease that inflames and narrows the airways. Asthma causes recurring periods of wheezing (a whistling sound when you breathe), chest tightness, shortness of breath, and coughing. The coughing often occurs at night or early in the morning.
Asthma affects people of all ages, but it most often starts during childhood.
Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Causes of Asthma
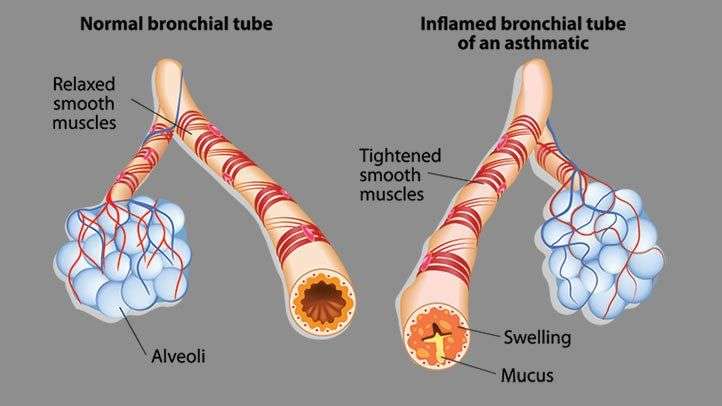
During an Asthmatic attack, airways (they are tubes that carry air into and out of your lungs) are inflamed. The inflammation makes the airways swollen and very sensitive. The airways tend to react strongly to certain inhaled substances.
When the airways react, the muscles around them tighten. This narrows the airways, causing less air to flow into the lungs. The swelling also can worsen, making the airways even narrower. Cells in the airways might make more mucus than usual. Mucus is a sticky, thick liquid that can further narrow the airways.
This chain reaction can result in asthma symptoms. Symptoms can happen each time the airways are inflamed.
Causes of Asthma attack
It isn’t clear why some people get asthma and others don’t, but it’s probably due to a combination of environmental and genetic (inherited) factors.
Asthma Triggers
Exposure to various substances that trigger allergies (allergens) and irritants can trigger signs and symptoms of asthma. Asthma triggers are different from person to person and can include:
- Airborne allergens, such as pollen, animal dander, mold, cockroaches and dust mites
- Respiratory infections, such as the common cold
- Physical activity (exercise-induced asthma)
- Cold air
- Air pollutants and irritants, such as smoke
- Certain medications, including beta blockers, aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen (Aleve)
- Strong emotions and stress
- Sulfites and preservatives added to some types of foods and beverages, including shrimp, dried fruit, processed potatoes, beer and wine
- Gastro esophageal reflux disease (GERD), a condition in which stomach acids back up into your throat
- Menstrual cycle in some women
Why Do You Get Asthma?
A number of factors are thought to increase the chances of developing asthma. These include:
- Having a blood relative (such as a parent or sibling) with asthma
- Having another allergic condition, such as atopic dermatitis or allergic rhinitis (hay fever)
- Being overweight
- Being a smoker
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
- Having a mother who smoked while pregnant
- Exposure to exhaust fumes or other types of pollution
- Exposure to occupational triggers, such as chemicals used in farming, hairdressing and manufacturing
Exposure to allergens, exposure to certain germs or parasites, and having some types of bacterial or viral infections also may be risk factors.
Symptoms of Asthma
Asthma symptoms range from minor to severe and vary from person to person. One may have infrequent asthma attacks; have symptoms only at certain times.
Some common symptoms are Asthma:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest tightness or pain
- Trouble sleeping caused by shortness of breath, coughing or wheezing
- A whistling or wheezing sound when exhaling (wheezing is a common sign of asthma in children)
- Coughing or wheezing attacks that are worsened by a respiratory virus, such as a cold or the flu
For some people, asthma symptoms flare up in certain situations:
- Exercise-induced asthma – which may be worse when the air is cold and dry,
- Occupational asthma – triggered by workplace irritants such as chemical fumes, gases or dust
- Allergy-induced asthma – triggered by particular allergens, such as pet dander, cockroaches or pollen
Based on the severity of the symptoms Asthmatic attack can be categorized as:
- Mild intermittent – Mild symptoms up to two days a week and up to two nights a month.
- Mild persistent – Symptoms more than twice a week, but no more than once in a single day
- Moderate persistent – Symptoms once a day and more than one night a week
- Severe persistent – Symptoms throughout the day on most days and frequently at night
Diagnosis of Asthma
Asthma diagnoses are based on three core components: a medical history, a physical exam, and results from breathing tests.
- Medical History: A detailed family history of asthma and allergies can help your doctor make an accurate asthma diagnosis. Your own personal history of allergies is also important as many are closely linked to asthma.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination will generally focus on the upper respiratory tract, chest, and skin. The high-pitched whistling sound while exhale – or wheezing – is a key sign of both an obstructed airway and asthma.
Skin will be examined for conditions such as eczema and hives, which have been linked to asthma.
- Breathing Test: Lung function tests, or pulmonary function tests – which measure how much air is breath in and out and how fast one can blow air out, physicians through Spirometry test.
Treatment for Asthma
Prevention and long-term control are key in stopping asthma attacks.
Treatment usually involves:
- Learning to recognize the triggers & taking steps to avoid them
- Breathing exercise to improve the lung capacity
- Medication for asthma is broadly categorized as either quick-relief medicine or long-term control medicine. Reducing airway inflammation and preventing asthma symptoms is the goal of long-term control medicines, where as immediate relief of asthma symptoms is the goal of quick-relief or “rescue” medicines.









