Treatment of Cirrhosis at HeyPills with our specially formulated Homeopathy treatment protocol includes customised homeopathic medicines for complete recovery without the need for liver transplant.
Homeopathy treatment of cirrhosis at Welling Homeopathy Clinics are tried and tested and proven to stop further progress of Liver Cirrhosis. Visit a Welling Clinic or consult online to know more about our Homeopathy treatment of Cirrhosis of Liver.
See our specialists at any heypills in India or order online instantly from the link above.
Why Choose Welling Homeopathy Medicines for
Liver Cirrhosis?
- Only Heypills custom-made Homeopathy medicines for cirrhosis can help you recover completely,
- The treatment has been developed at Welling research labs to work faster than traditional homeopathy, and stops further progression of liver cirrhosis,
- The Homeopathy treatment for liver cirrhosis can help stop complications of cirrhosis like liver cancer,
- The treatment has helped over 3200 patients suffering from liver cirrhosis from 108 countries,
Consult our specialists today for a detailed evaluation and to start your customised Homeopathy medicines for liver cirrhosis. Call +91 9999064336 to order online or book an appointment.
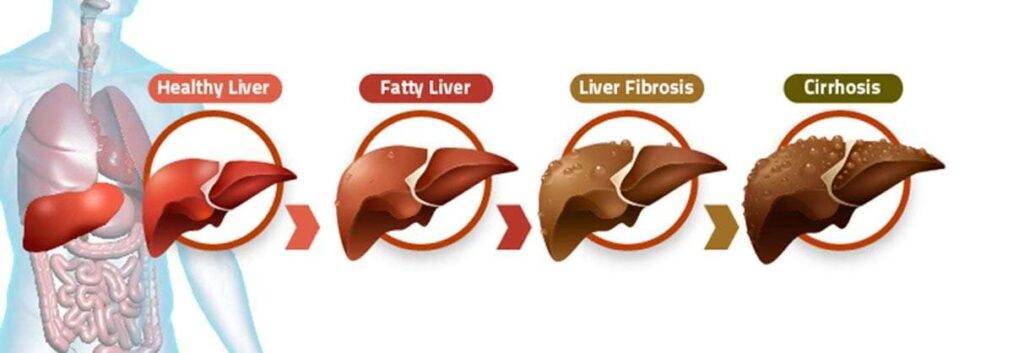
What is Cirrhosis of Liver ?
Cirrhosis is a condition in which the liver does not function properly due to long-term damage. Typically, the disease comes on slowly over months or years. Early on, there are often no symptoms. Cirrhosis is a complication of liver disease which involves loss of liver cells and irreversible scarring of the liver.

In the early stages of cirrhosis, the liver continues to function. However, as cirrhosis gets worse and scar tissue replaces more healthy tissue, the liver will begin to fail. Chronic liver failure, which is also called end-stage liver disease, progresses over months, years, or even decades. With end-stage liver disease, the liver can no longer perform important functions or effectively replace damaged cells.
Cirrhosis is an increasing cause of morbidity and mortality in more developed countries, being the 14th most common cause of death worldwide but fourth in central Europe
Cause of Cirrhosis
Chronic Hepatitis C
Alcohol-related liver disease. Research suggests that drinking two or fewer drinks a day for women and three or fewer drinks a day for men may not injure the liver.3 Drinking more than these amounts leads to fat and inflammation in the liver, which over 10 to 12 years can lead to alcoholic cirrhosis.4
Hepatitis C. is a common cause of cirrhosis in Western Europe, North America, and many other parts of the world. Cirrhosis can also be caused by hepatitis B and D.
Autoimmune hepatitis
Genetic Conditions
- Hemochromatosis– iron accumulates in the liver and other parts of the body.
- Wilson’s disease – copper accumulates in the liver and other parts of the body.
- Budd-Chiari syndrome
- There is thrombosis (blood clots) in the hepatic vein, the blood vessel that carries blood from the liver, leading to liver enlargement and the development of collateral vessels.
Why You Get Liver Cirrhosis?
There are several known risk factors for developing cirrhosis. The most common risk factors are:
- Excess alcohol use – regular consumption of more than 1-2 alcoholic beverage a day for women or 2-3 alcoholic beverages a day for men over a long period of time can lead to liver cirrhosis. Patients with other risk factors for liver disease may develop cirrhosis with even less regular alcohol use.
- Infection with viral hepatitis – while not all patients who have chronic infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV) or the hepatitis C virus (HCV) will develop cirrhosis, chronic viral hepatitis is one of the leading causes of liver disease in the world.
- Obesity and Diabetes – obesity and diabetes are both risk factors for a form of liver injury known as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Over time NASH can lead to significant liver injury and cirrhosis. Not all patients with obesity or diabetes will develop NASH.
Signs and Symptoms of Cirrhosis
Symptoms come on gradually as the liver loses its ability to work properly. They include:
- tiredness and weakness
- bruising easily
- itchy skin
- yellowing of skin and whites of eyes (jaundice)
- fluid buildup in abdomen (ascites)
- appetite loss
- nausea and vomiting
- swelling in legs (oedema)
- weight loss
- very black, dark or tarry stool (poo)
- confusion, drowsiness and slurred speech
- fever and shivering
Spider-like blood vessels on skin.
Danger Symptoms where medical help should be received immediately
- fever with high temperatures and shivers, often caused by an infection
- shortness of breath
- vomiting blood
- very dark or black tarry stools (faeces)
- periods of mental confusion or drowsiness.
Although these symptoms may seem very different, because your liver is responsible for so many different functions, if it stops working properly, a range of problems can result.
Complications of Liver Cirrhosis
- High blood pressure in the veins that supply the liver (portal hypertension).Cirrhosis slows the normal flow of blood through the liver, thus increasing pressure in the vein that brings blood from the intestines and spleen to the liver.
- Swelling in the legs and abdomen.Portal hypertension can cause fluid to accumulate in the legs (edema) and in the abdomen (ascites). Edema and ascites also may result from the inability of the liver to make enough of certain blood proteins, such as albumin.
- Enlargement of the spleen (splenomegaly).Portal hypertension can also cause changes to the spleen. Decreased white blood cells and platelets in your blood can be a sign of cirrhosis with portal hypertension.
- Portal hypertension can cause blood to be redirected to smaller veins, causing them to increase in size and become varices. Strained by the extra load, these smaller veins can burst, causing serious bleeding. Life-threatening bleeding most commonly occurs when veins in the lower esophagus (esophageal varices) or stomach (gastric varices) rupture. If the liver can’t make enough clotting factors, this also can contribute to continued bleeding. Bacterial infections are a frequent trigger for bleeding.
Other complications of Liver Cirrhosis
- If you have cirrhosis, your body may have difficulty fighting infections. Ascites can lead to spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, a serious infection.
- Cirrhosis may make it more difficult for your body to process nutrients, leading to weakness and weight loss.
- Buildup of toxins in the brain (hepatic encephalopathy).A liver damaged by cirrhosis isn’t able to clear toxins from the blood as well as a healthy liver can. These toxins can then build up in the brain and cause mental confusion and difficulty concentrating. Hepatic encephalopathy symptoms may range from fatigue and mild impairment in cognition to unresponsiveness or coma.
- Jaundice occurs when the diseased liver doesn’t remove enough bilirubin, a blood waste product, from your blood. Jaundice causes yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes and darkening of urine.
- Bone disease.Some people with cirrhosis lose bone strength and are at greater risk of fractures.
- Increased risk of liver cancer.A large proportion of people who develop liver cancer that forms within the liver itself have cirrhosis.
- Acute-on-chronic liver failure.Some people end up experiencing multiorgan failure. Researchers now believe this is a distinct complication in some people who have cirrhosis, but they don’t fully understand its causes.
Investigations For Cirrhosis
Blood tests to check liver function
Measuring the levels of certain chemicals produced by the liver can show how well your liver is working. Blood tests may be used to measure:
- Albumin and total serum protein. Albumin is a type of protein. Liver disease can cause a decrease in protein levels in the blood.
- Partial thromboplastic timeor prothrombin time/INR. These tests measure blood-clotting factors that are produced in the liver.
- Bilirubin. This is produced when the liver breaks down hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying substance in red blood cells. Cirrhosis may cause high bilirubinlevels, which causes jaundice.
Blood tests to check for inflammation of the liver
You may have blood tests to check your liver enzymes. These can help show whether you have had liver inflammation for a long time. These blood tests include:
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). An increased level of these enzymes may mean injury to the liver and the death of liver cells.
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP). An increased ALP level may mean blockage of bile ducts.
- Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT). An increased level can happen because of alcohol use or diseases of the bile ducts.
Some people with cirrhosis have normal liver enzymes.
People who have cirrhosis sometimes don’t have symptoms until liver damage is extensive. Symptoms of cirrhosis and its complications may include:
- Fatigue.
- Yellowing of the skin(jaundice).
- Itching.
- Swelling from fluid buildup in the legs (edema).
- Bruising easily and having heavy nosebleeds.
- Redness of the palms.
- Small red spots and tiny lines on the skin called spider angiomas.
- Weight loss and muscle wasting.
- Belly pain or discomfort.
- Frequent infections.
Scar tissue from cirrhosis may block the proper flow of blood from the intestines through the liver. The scarring can lead to increased pressure in the veins that supply this area. This is called portal hypertension. It can lead to other complications, which may include:
- Fluid buildup in the belly (ascites).
- Bleeding from enlarged veins (varices) in the digestive tract. This is called variceal bleeding.
- Increased spleen This can lead to a low blood platelet count.
- Infection of the fluid in the belly (spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, or SBP).
- Altered brain function (encephalopathy). This usually only occurs in people who have advanced portal hypertension.
- Hepatorenal syndrome.Kidney (renal) failure can occur in cases of advanced liver d
- Hepatopulmonary syndrome. Portal hypertension can cause lung problems, such as widening of the blood vessels in the lungs. This causes the blood to move too swiftly through the lungs to pick up enough oxygen.
- Hepatic hydrothorax. Fluid can build up between the lungs and the chest (pleural effusion) and press on the lungs.
Tests that show an image of the liver
Imaging tests can check for tumors and blocked bile ducts. They also can be used to look at liver size and blood flow through the liver. These tests include:
- Abdominal ultrasound.
- CT scan of the abdomen (including the liver, gallbladder, and spleen).
- MRI scan of the abdomen
Allopathic Treatment of Liver Cirrhosis
Specific medical therapies may be applied to many liver diseases in an effort to diminish symptoms and to prevent or forestall the development of cirrhosis. Examples of such treatments include the following:
- Prednisone and azathioprine – For autoimmune hepatitis
- Interferon and other antiviral agents – For hepatitis B and C
- Phlebotomy – For hemochromatosis
- Ursodeoxycholic acid – For primary biliary cirrhosis
- Trientine and zinc – For Wilson disease
Once cirrhosis develops, treatment is aimed at the management of complications as they arise. Examples include the following:
- Hepatorenal syndrome – Kidney function usually recovers when patients with cirrhosis and hepatorenal syndrome undergo liver transplantation; patients with early hepatorenal syndrome may be salvaged by aggressive expansion of intravascular volume with albumin and fresh frozen plasma and by avoidance of diuretics
- Hepatic encephalopathy – Pharmacologic treatment includes the administration of lactulose and antibiotics
- Ascites – Treatment can include sodium restriction and the use of diuretics, large-volume paracentesis, and shunts (peritoneovenous, portosystemic, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic)
Liver transplantation
Patients should be referred for consideration for liver transplantation after the first signs of hepatic decompensation.
Homeopathic Treatment of Liver Cirrhosis
Homeopathic medicine treat the underlying cause of cirrhosis of liver such as viral infections, genetic tendency, Bad effects of alcohol and metabolic changes .
Helps to control the scarring of tissues. And if homoeopathy has started at the early stage(compensated stage ) it is possible to restore the altered function of the liver .
And if it is started at a later stage it can halt the further progress of the disease and prevent the patient from getting into the complication of portal hypertension.
Homeopathy can be started at any stage of the cirrhosis early or late, depending upon when one has chosen to opt for Homeopathy or depending upon till what stage disease has progressed.It can differentially give an individual a better quality of life by allaying his pain and reducing his discomfort.
Best Five Homeopathy Remedies for Liver Cirrhosis
As a senior Homeopathy doctor, I would like to recommend the five best Homeopathy remedies for liver cirrhosis. These remedies are selected based on their effectiveness in treating the specific symptoms and personality traits of the patient. Here they are:
- Nux Vomica: This remedy is best suited for individuals who have a history of alcohol or drug abuse. They tend to be irritable, easily angered, and have a strong desire for stimulants like coffee or alcohol. Other symptoms include constipation, indigestion, and a general feeling of discomfort after eating.
- Lycopodium: This remedy is useful for patients who experience bloating and distention in the abdomen, especially after eating. They may also have a strong craving for sweets and warm drinks. Personality-wise, they tend to be introverted, lack confidence, and have a fear of public speaking.
- Carduus Marianus: This remedy is specific to liver disorders and is effective in treating liver cirrhosis. Patients who benefit from this remedy tend to have a history of alcohol abuse, have a swollen liver, and experience discomfort in the right upper abdomen. They may also experience nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite.
- Chelidonium: This remedy is useful for patients who experience pain and discomfort in the right upper abdomen, which may radiate to the back or right shoulder. They may also have a yellowish tint to their skin or eyes, indicating liver dysfunction. Personality-wise, they tend to be irritable and easily angered.
- Natrum Sulphuricum: This remedy is effective in treating liver cirrhosis in patients who have a history of hepatitis or other liver infections. They tend to experience bloating and discomfort in the abdomen, have a bitter taste in their mouth, and feel worse in damp weather. Personality-wise, they tend to be reserved and may suffer from depression.
It is important to note that Homeopathy remedies should be prescribed based on the individual symptoms and personality traits of the patient. Therefore, it is recommended to consult with our qualified Homeopathy practitioner before taking any remedies.








