Treatment of Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) with natural custom-made Homeopathy medicines can cure your symptoms of IBD completely.
Inflammatory bowel disease is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the gastrointestinal tract that can affect any part of the digestive system, from mouth to anus. The cause of IBD is unknown; however, scientists believe it may be caused by an abnormal immune response in genetically susceptible people. There are two types: Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis.
Symptoms include diarrhoea, fever, weight loss and pain or discomfort in the abdomen area. Treatment options for IBD depend on the severity of symptoms and range from medications such as steroids to surgery. But what if you could avoid all that?
Types of Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Homeopathy Treatment of Crohn’s Disease
Homeopathy Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis
Why Homeopathic Medicines for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Treatment?
- Our custom-made Homeopathy medicines for Inflammatory bowel disease has helped 12,230 patients since the start of the clinic,
- The Homeopathy treatment for Inflammatory bowel disease has cured the most widespread painful Inflammatory bowel disease,
- The treatment is non-steroidal, surgery or hospital visits. Just natural Homeopathy medicines custom-made for you for faster recovery and complete cure,
- Usually, we see a cure in 12-18 months, rarely requiring 24 months.
- The fastest and the safest way to get cured of Inflammatory bowel disease symptoms permanently.
Call +91 9999064336 to book an appointment or to consult and order online. Consult our specialists today for a detailed evaluation and to start your customised Homeopathy medicines for Inflammatory bowel disease.
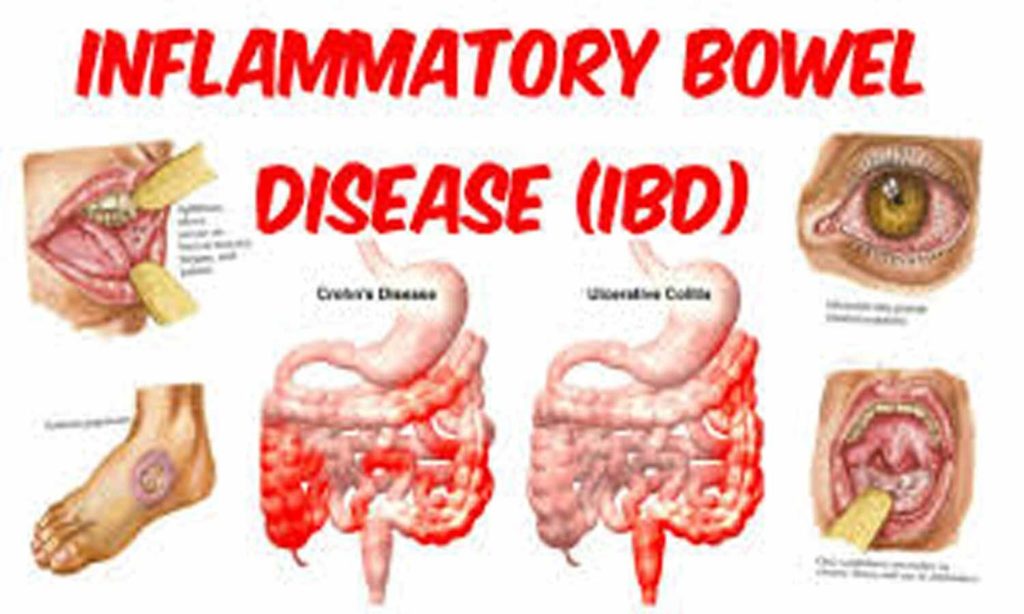
What is Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a term that encompasses the inflammatory conditions of the gastrointestinal tract. Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are types of IBD. These diseases are chronic, meaning that they can remain active or inactive for long periods of time.
It is impossible to know the exact cause of inflammatory bowel disease, which makes it difficult to determine how much one’s diet and lifestyle contribute to the development of IBD. That said, there are several things you can do to reduce your risk of developing IBD.
Follow a healthy diet plan that excludes junk food but is rich in fiber, fruits and vegetables
Exercise regularly, as this can reduce inflammation and strengthen the immune system
Keep your weight down if you are overweight or obese, as excess pounds put additional stress on the digestive tract
Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol excessively as these substances havebeen linked to IBD
Get tested for Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis if there is a family history of the illnesses as this can help identify whether you are at higher risk of developing IBD. The earlier inflammatory bowel disease is diagnosed, the homeopathy treatment cn help you get cured.
If you have been experiencing symptoms that may be related to IBD, such as persistent diarrhea or abdominal cramps, make an appointment with your doctor to be screened for the disease.
What Are The Symptoms of IBD?
Symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease may include:
– Abdominal pain and cramping
– Rectal bleeding and blood in the stool (indicates a high level of inflammation)
– Diarrhea that may be bloody, mucus-filled or watery
– Anemia due to chronic bleeding
– Weight loss
IBD can cause complications outside of the gastrointestinal tract, including arthritis or inflammation in the eyes, joints or skin. These symptoms may indicate a separate condition related to IBD. If you are experiencing any of these problems it is importantto tell your doctor.
How to Reduce Your Risk Of Getting IBD
If you are at risk of developing inflammatory bowel disease there are certain steps you can take to lower that risk, including:
– Get tested for Crohn’s Disease or ulcerative colitis if it runs in the family as this can help identify whether you are at higher risk of developing IBD. The earlier inflammatory bowel disease is diagnosed, the better chance you have of getting cured
– Follow a healthy diet plan that excludes junk food but is rich in fibre, fruits and vegetables
– Exercise regularly, as this can reduce inflammation and strengthen the immune system
– Keep your weight down if you are overweight or obese, as excess pounds put additional stress on the digestive tract
– Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol excessively as these substances have been linked to IBD.
Risks And Complications Of IBD
IBD can cause complications outside of the gastrointestinal tract, including arthritis or inflammation in the eyes, joints or skin. These symptoms may indicate a separate condition related to IBD. If you are experiencing any of these problems it is important to tell your doctor.
IBD can cause complications within the gastrointestinal tract, including:
– Ulcers and sores in the lining of the intestines that may bleed or produce pus
– Perforated or weakened areas of intestine (bowel obstructions) whichwill require surgery to repair
– Fistulas (abnormal passageways between organs)
– Inflammation of the liver or biliary system (this can lead to jaundice, nausea and vomiting)
Preventative Care For Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
If you are at risk for inflammatory bowel diseases it is important to take precautionary steps to avoid the illness. Follow a healthy diet, exercise regularly and keep your weight under control if necessary. Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol excessively as these substances have been linked to IBD.
Types of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
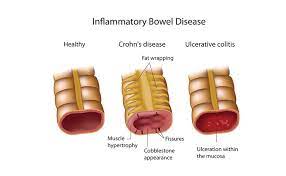
The two types of inflammatory bowel diseases that are most common are ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic condition that affects the colon, producing open sores or ulcers within its lining. The symptoms of ulcerative colitis include diarrhea, abdominal cramping, pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, bleeding from the rectum, weight loss, fever sometimes caused by infections.
Crohn’s disease is an inflammation of the lining of any part of your digestive tract including your mouth, esophagus, stomach and small intestine. Unlike ulcerative colitis which has limited effects on your digestive system, Crohn’s can affect any part of it. Symptoms include problems with fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, pain in the abdomen, weight loss and diarrhoea.
Other types of inflammatory bowel disease include indeterminate colitis or collagenous colitis which are very rare.
Symptoms of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Symptoms of inflammatory bowel diseases include abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, weight loss, and diarrhoea. Inflammatory bowel diseases cause the intestines to become inflamed.
For Crohn’s disease, there are typically periods of remission and flare ups. The disease can be caused by an overactive immune system that attacks the intestine.
Ulcerative colitis is another inflammatory bowel disease that causes ulcers in the large intestines. Ulcerative colitis affects the lining of the large intestines
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are closely related inflammatory bowel diseases that cause abdominal pain, diarrhoea, rectal bleeding, and other symptoms. Both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can lead to further complications if left untreated.
Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases vary depending on the severity of the condition. There are different types of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Ulcerative colitis is a chronic, long-term disease in which the lining of the large intestine becomes inflamed with ulcers and sores
The treatment for this can be
A) Medications
B) Surgery
C) Liver transplantation.
Crohn’s disease, also known as regional enteritis, is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) type that can affect any part of the digestive tract from mouth to anus. It can cause layers of deep tissue to swell and form the pus-filled sacs of ileitis, a condition called “fistulas.” Severe inflammation can cause scarring and stiffening in the intestinal wall so that it is not able to do its job.
In the treatment of Crohn’s Disease, there are three options
A) Medication
B) Removing part of the bowel
C) Surgery
A person with inflammatory bowel disease may need to take medication for a long time. There are many different types of medications available and treatment must be individualized for each patient. Some people will require only one type of medication, while others may need a combination of several, including
Corticosteroids: Oral and injected corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and swelling. However, they must be used carefully because they can cause side effects such as high blood pressure and other cardiovascular problems; osteoporosis (thinning of the bones); diabetes; weight gain; muscle weakness; mood swings, irritability, and insomnia.
The above medications may have significant adverse effects, and many patients cannot tolerate them.
Other treatments: Other medications that can be used to treat IBD include Imuran (azathioprine), a drug that suppresses the immune system; Remicade (infliximab), an antibody to TNF-alpha; and Pentasa (mesalamine), which is taken as an enema or suppository.
Although these medications may be used to treat IBD, many patients cannot tolerate them either because of significant adverse effects.
Surgery: In certain forms of IBD, particularly Crohn’s Disease, surgery must be considered if medical treatment fails and the patient is in danger from the disease process.
Medications for IBD are given either orally or by injection. Patients with ulcerative colitis usually respond to oral medications, although some may require regular injections of corticosteroids or other drugs into the rectum. Even if they responded well to medication at first, many patients eventually need surgery because their disease tends to return after treatment is stopped
Infliximab, a drug that suppresses the immune system, is one of several medications used to treat Crohn’s Disease. This can be given intravenously or by injection into the muscle every few weeks. Infliximab has been shown in clinical trials to induce remission in 50% of patients with moderate to severe disease. The advantages of infliximab are that it is effective and the drug can be delivered by injection at home rather than in a hospital. Patients need to be monitored regularly because about 5% of them develop serious infections such as tuberculosis or fungal infections, which may require treatment with medications other than infliximab.








